CLASS:
NR305 – Health Assessment for the Practicing RN
NR305 Week 4 Discussion: iHuman Virtual Patient Encounter Debriefing
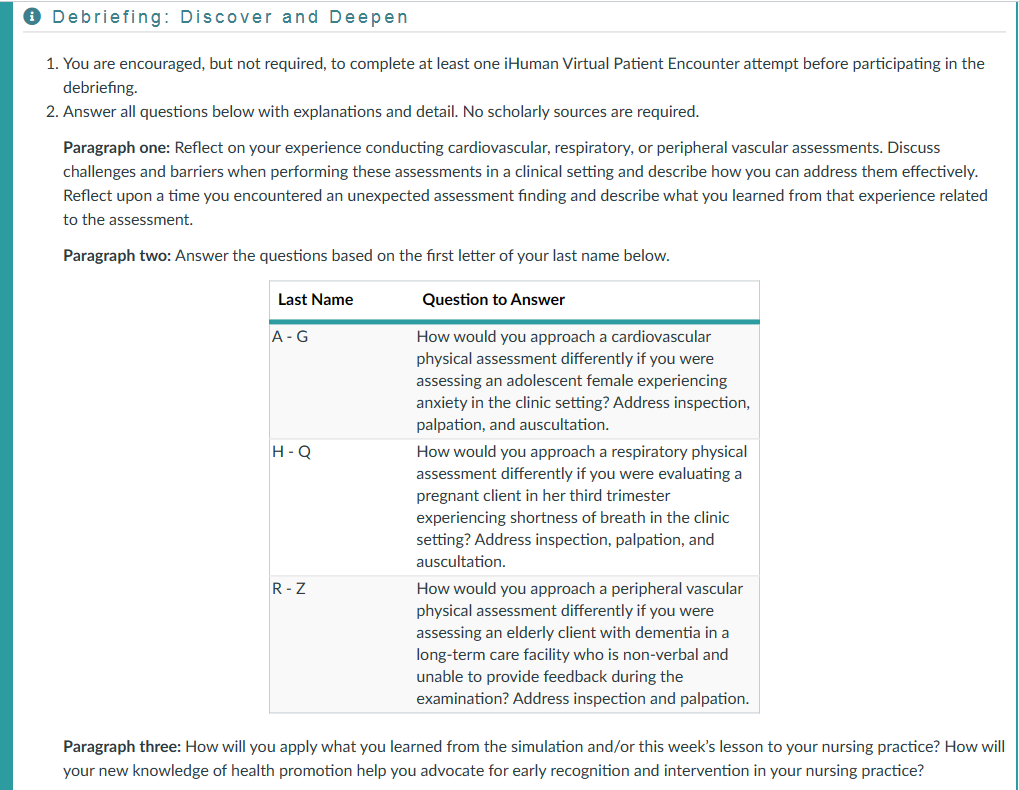
- You are encouraged, but not required, to complete at least one iHuman Virtual Patient Encounter attempt before participating in the debriefing.
- Answer all questions below with explanations and detail. No scholarly sources are required.
Paragraph one: Reflect on your experience conducting cardiovascular, respiratory, or peripheral vascular assessments. Discuss challenges and barriers when performing these assessments in a clinical setting and describe how you can address them effectively. Reflect upon a time you encountered an unexpected assessment finding and describe what you learned from that experience related to the assessment.
Paragraph two: Answer the questions based on the first letter of your last name below.
| Last Name | Question to Answer |
|---|---|
| A – G | How would you approach a cardiovascular physical assessment differently if you were assessing an adolescent female experiencing anxiety in the clinic setting? Address inspection, palpation, and auscultation. |
| H – Q | How would you approach a respiratory physical assessment differently if you were evaluating a pregnant client in her third trimester experiencing shortness of breath in the clinic setting? Address inspection, palpation, and auscultation. |
| R – Z | How would you approach a peripheral vascular physical assessment differently if you were assessing an elderly client with dementia in a long-term care facility who is non-verbal and unable to provide feedback during the examination? Address inspection and palpation. |
Paragraph three: How will you apply what you learned from the simulation and/or this week’s lesson to your nursing practice? How will your new knowledge of health promotion help you advocate for early recognition and intervention in your nursing practice?
SOLUTION
Paragraph One:
Reflecting on my experience with cardiovascular, respiratory, and peripheral vascular assessments, one significant challenge is effectively communicating with patients who may feel anxious or uncomfortable, which can influence their responses or physiological measurements. For example, during auscultation, an anxious patient may have an elevated heart rate or…………………………………….purchase at $5
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.