NR566 Week 4: Midterm Exam

A 70-year-old immunocompromised patient with mild COVID-19 presents within 3 days of symptoms. Which therapy is MOST appropriate to reduce progression to severe disease?
Answers: A – D
A. Ritonavir
B. Ribavirin
C. ⭐ Monoclonal antibody
D. Dexamethasone
A patient prescribed bethanechol for urinary retention develops abdominal cramping and diarrhea. What is the BEST explanation?
A Muscarinic receptor stimulation in the gastrointestinal tract
B Parasympathetic blockade
C Drug toxicity inducing dumping syndrome
D Allergic reaction induced fluid shifts
What is the mechanism of action of carbapenems?
A. Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
B. Inhibition of cell wall synthesis ✔️
C. Inhibition of protein synthesis
D. Disruption of cell membrane integrity
A patient with HIV infection develops symptoms of lactic acidosis. Which class of antiretroviral drugs is MOST likely responsible for this adverse effect?
A. Integrase strand transfer inhibitors
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Protease inhibitors
D. Nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors ✔️
Which cephalosporin can induce a disulfiram-like reaction if alcohol is consumed?
A Cefotetan
B Cefazolin
C Ceftriaxone
D Cefuroxime
A patient is prescribed clindamycin for a suspected bacterial infection. Which of the following instructions should the NP provide to the patient regarding the potential adverse effects of clindamycin?
A. Report any episodes of constipation
B. Expect mild gastrointestinal discomfort, which is common with clindamycin use
C. Monitor for signs of skin rash or itching
D. Promptly report any diarrhea to the healthcare provider
When is sensitivity testing MOST likely to be performed for antibiotic selection?
A. When resistance is unlikely in the infecting organism
B. When resistance is common in the infecting organism
C. When the infecting organism is unknown
D. When previous allergic reactions are reported
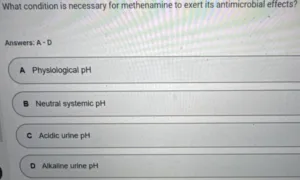
Which drug class should be avoided in combination with methenamine to prevent reduced antibacterial effects?
A. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
B. ✔️ Urinary alkalinizers
C. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
D. Beta-lactam antibiotics……………………………please add to cart and check out to access this entire exam at $50 only




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.